Explore Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud Computing Architecture:
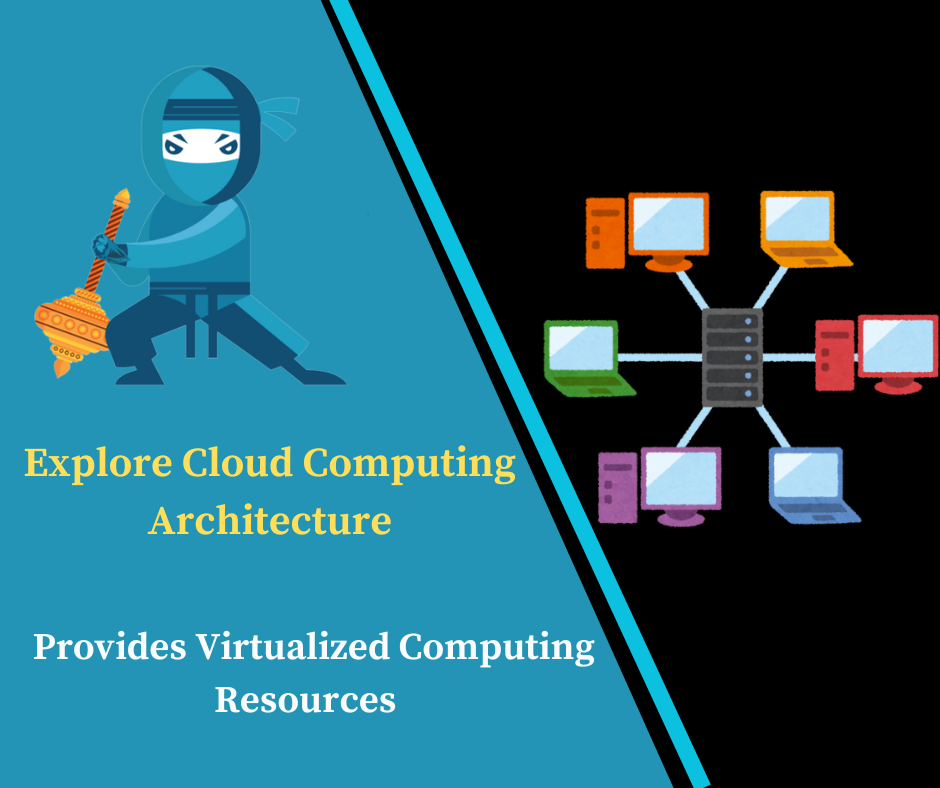
Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and subcomponents required for cloud computing. It encompasses everything from the front-end user interface to the back-end storage, and all the software, middleware, and services that connect them.
Cloud computing architecture is designed to provide on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources, including networks, servers, storage, applications, and services. It offers several deployment models (public, private, hybrid) and service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), each catering to different user needs and business requirements.
Components of Cloud Computing Architecture
1. Frontend and Backend Layers:
Frontend: This is the client-side interface that users interact with to access cloud services. It includes applications and interfaces that facilitate user interaction.
Backend: The backend consists of the cloud infrastructure itself, including servers, storage, virtual machines, and networks. It is managed and maintained by the cloud service provider.
2. Cloud Infrastructure:
Data Centers: Physical facilities housing servers, storage devices, and networking equipment that form the backbone of cloud services.
Virtualization: Technology that abstracts physical resources into virtual resources, enabling multiple virtual machines or containers to run on a single physical machine.
Networking: Includes routers, switches, load balancers, and other networking components that facilitate communication between cloud resources and users.
Also read: What is Cloud Computing Services and Cloud Computing Services
3. Cloud Services:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking.
Also read: Cloud Computing Services Platform
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with underlying infrastructure complexities.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for users to install and maintain software locally
4. Cloud Orchestration:
Automation: Tools and frameworks that automate the provisioning, configuration, and management of cloud resources, ensuring scalability, efficiency, and consistency.
Management: Centralized management consoles and APIs that enable administrators to monitor, control, and optimize cloud infrastructure and services.
5. Security and Compliance:
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls access to cloud resources based on user roles, ensuring data security and regulatory compliance.
Encryption: Protects data by encrypting it during storage and transmission, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
Compliance: Adheres to industry regulations and standards to ensure data privacy, security, and integrity.
6. Performance Optimization:
Monitoring: Tracks performance metrics to optimize application performance.
CDNs (Content Delivery Networks): Improves content delivery speed and reliability.
7. Backup and Disaster Recovery:
Data Backup: Regular backups to prevent data loss.
Disaster Recovery: Plans and technologies to recover data and resume operations after disasters.
8. APIs and Integration:
APIs: Interfaces for integrating cloud services with applications and systems.
Integration: Connects cloud services with on-premises and third-party applications.
1.IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It delivers fundamental computing infrastructure such as virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking resources as a service.
Characteristics:
Scalability: Users can scale resources up or down based on demand.
Management: Users have control over operating systems, applications, and runtime environments.
Flexibility: Offers a wide range of infrastructure components that can be customized and managed by the user.
Use Cases:
Best suited for businesses that require flexible and scalable infrastructure without the need to invest in physical hardware.
Ideal for development and testing environments, hosting websites and applications, and running batch processing workloads.
Examples:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine.
PaaS (Platform as a Service
PaaS provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
Characteristics:
Abstraction: Abstracts away infrastructure management tasks such as hardware provisioning, operating system maintenance, and middleware setup.
Development Tools: Offers development tools, databases, middleware, and runtime environments as integrated services.
Deployment: Simplifies the deployment process with automated scaling and management of applications.
Use Cases:
Ideal for developers and teams focusing on application development, as it accelerates time to market by eliminating infrastructure management overhead.
Suitable for building and deploying web applications, mobile backends, and API services.
Examples:
Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service, Google App Engine.
3.SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access applications via a web browser without needing to install or maintain software locally.

Characteristics:
Accessibility: Accessible from any device with internet connectivity.
Updates: Software updates and maintenance are handled by the service provider.
Multi-tenancy: Typically serves multiple customers (tenants) from a single instance of the application.
Use Cases:
Suitable for businesses and end-users looking to use applications without the upfront costs and complexity of purchasing and managing software licenses.
Commonly used for email services, customer relationship management (CRM), collaboration tools, and productivity applications.
Examples:
Salesforce (CRM), Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), Microsoft 365 (Office 365).
Key Differences
Scope: IaaS provides raw infrastructure components, PaaS offers a platform for application development, and SaaS delivers fully functional applications.
Management: With IaaS, users manage virtual machines, storage, and networking. In PaaS, users focus on application development while the provider manages the platform. SaaS requires no management as applications are fully managed by the provider.
Customization: IaaS offers the highest level of customization, followed by PaaS, which provides some customization within the application development environment. SaaS applications are standardized and offer limited customization options.
Deployment: IaaS and PaaS require user involvement in deployment and management tasks. SaaS applications are ready to use with minimal deployment effort.
FAQ:
What are the benefits of cloud computing architecture?
Cloud architecture provides scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility, and allows for rapid deployment of services and applications.
How secure is cloud computing architecture?
Security measures such as data encryption, access controls, and regular audits are implemented to protect data and resources in cloud architectures.
What are the different deployment models in cloud computing architecture?
Public cloud (services provided by third-party providers over the public internet), private cloud (dedicated infrastructure for a single organization), and hybrid cloud (combination of public and private clouds).
Conclusion:
Cloud computing architecture is a fundamental framework that enables businesses and individuals to leverage powerful computing resources without the need for owning or managing physical hardware. It facilitates innovation, agility, and cost-effectiveness, making it a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure.